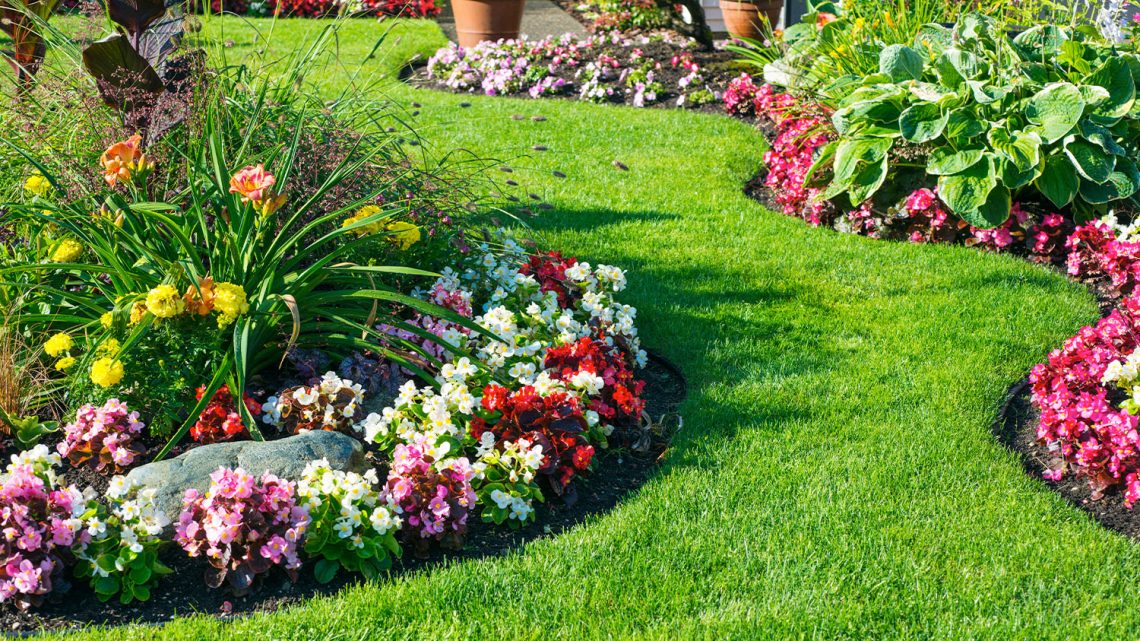
Flowering plants, or angiosperms, represent one of the most diverse and ecologically significant groups of organisms on Earth. They encompass a wide range of species, from the tiniest wildflowers to towering trees, all characterized by their ability to produce flowers and seeds enclosed within a fruit https://mojdomowyazyl.pl. This article delves into the biology, ecology, and cultural significance of flowering plants, highlighting their vital roles in ecosystems and human societies.
Classification and Diversity
Flowering plants belong to the kingdom Plantae and are classified under the phylum Angiosperms. They can be broadly categorized into two main groups: monocots and dicots.
- Monocots: These plants, which include grasses, lilies, and orchids, typically have one seed leaf (cotyledon), parallel leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of three. They often exhibit fibrous root systems.
- Dicots: In contrast, dicots, such as roses, sunflowers, and oaks, have two cotyledons, net-like leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of four or five. They generally have a taproot system.
Angiosperms are the largest group of plants, with over 300,000 species identified. This incredible diversity allows them to inhabit a wide range of ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to arid deserts.
Structure and Function
The structure of flowering plants is intricately designed to facilitate reproduction. The key components of a flower include:
- Petals: Often brightly colored and fragrant, petals attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds.
- Stamens: These are the male reproductive organs, consisting of anthers that produce pollen.
- Carpels: The female reproductive parts, including the ovary, style, and stigma, where pollen germinates and fertilization occurs.
Once fertilization takes place, the ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. Fruits can take many forms, from fleshy berries to dry pods, each adapted to specific dispersal mechanisms, such as wind, water, or animal ingestion.
Ecological Importance
Flowering plants play crucial roles in ecosystems. They are primary producers, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis and forming the base of food webs. They provide food and habitat for countless organisms, including insects, birds, and mammals.
Moreover, flowering plants are essential for maintaining soil health and preventing erosion. Their root systems stabilize the soil, while their leaves and flowers contribute to nutrient cycling. Many flowering plants also produce chemicals that can deter herbivores or attract beneficial insects, illustrating complex ecological interactions.
Pollination: A Symphony of Cooperation
Pollination is a critical process in the life cycle of flowering plants, facilitating genetic diversity and reproduction. While many plants rely on wind for pollination, an estimated 75% depend on animals, particularly insects.
Bees, butterflies, and birds are attracted to flowers by their colors and scents. As they collect nectar and pollen, they inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another, leading to fertilization. This mutualistic relationship benefits both parties: plants gain reproductive success, while pollinators receive food.
However, many flowering plants face challenges due to declining pollinator populations, primarily caused by habitat loss, pesticides, and climate change. Conservation efforts focusing on preserving habitats and promoting pollinator-friendly practices are vital to sustain these essential relationships.
Cultural Significance
Throughout history, flowering plants have held deep cultural significance for humans. They are symbols of beauty, love, and renewal, often featured in art, literature, and religious rituals. Many cultures celebrate specific flowering plants during festivals or as part of traditional medicine practices.
Additionally, flowering plants are integral to agriculture. They provide fruits, vegetables, grains, and ornamental plants, supporting economies and food systems worldwide. The cultivation of flowering plants for food and aesthetics has shaped landscapes and societies for centuries, emphasizing their importance in our daily lives.