Woodworking is an ancient craft that has evolved over centuries, from primitive hand tools to highly sophisticated machinery. In today’s modern woodworking industry, machinery plays a crucial role in increasing precision, efficiency, and the quality of finished products CNC Router. This article explores the various types of woodworking machinery, their applications, and how they have transformed the craft.
The Evolution of Woodworking Machinery
The transition from hand tools to machinery in woodworking began in the early 19th century, powered by the Industrial Revolution. Initially, steam engines were used to drive large woodworking machines, which allowed for greater output and faster production times. Over time, advancements in technology, such as the introduction of electric motors and computer-controlled systems, further revolutionized woodworking machinery, making it more accessible and efficient for smaller workshops and larger commercial enterprises alike.
Today, woodworking machinery encompasses a wide range of equipment that assists with cutting, shaping, sanding, and finishing wood. The integration of computer numerical control (CNC) technology has allowed for even higher precision and customization in wood products, making modern woodworking machinery indispensable to the industry.
Types of Woodworking Machinery
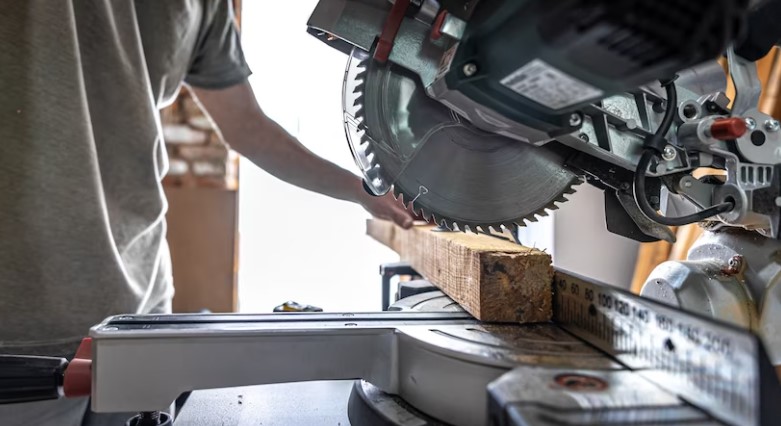
1. Table Saws
The table saw is one of the most essential woodworking machines. It consists of a circular blade mounted on an arbor that protrudes through a table. This machine is primarily used for cutting large pieces of wood into smaller, more manageable sizes. Table saws come in various sizes, from portable models for smaller jobs to industrial models that can handle large-scale operations.
Key uses: Cross-cutting, rip-cutting, bevel cuts, and making dado or groove cuts.
2. Band Saws
The band saw is a versatile machine featuring a long, continuous band of toothed metal that moves in a loop around two or more pulleys. It is known for its ability to make both straight and curved cuts, making it a popular choice for intricate and detailed work.
Key uses: Resawing wood, cutting curves, and making intricate cuts on smaller wood pieces.
3. Planers
Wood planers are used to smooth and flatten rough-sawn timber, creating uniform thickness across the entire length of a board. They are indispensable for any woodworking project requiring consistent thickness and a smooth surface. There are two main types: handheld and stationary planers.
Key uses: Smoothing rough timber, dimensioning wood to specific thicknesses, and removing imperfections from surfaces.
4. CNC Routers
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) routers have revolutionized woodworking by providing a level of precision that manual routers could never achieve. These machines use computer software to control a router’s movement and can carve, cut, and engrave detailed patterns in wood.
Key uses: Complex cuts, engraving, sign-making, and 3D carving.
5. Lathes
Wood lathes are machines used to turn wood pieces, such as legs for furniture or spindle designs, at high speeds. The wood is held in place while the operator uses tools to shape it into cylindrical or symmetrical designs. Modern lathes can be automated to produce highly precise shapes.
Key uses: Shaping round or cylindrical objects, turning spindles, and making intricate patterns.
6. Sanding Machines
Sanding machines, also known as sanders, are used to smooth rough surfaces, remove imperfections, and prepare wood for finishing. There are various types of sanders, including belt sanders, orbital sanders, and drum sanders, each suited for specific applications.
Key uses: Surface smoothing, preparation for finishing, and removing blemishes or rough patches.
7. Jig Saws
Jig saws are portable cutting tools with a straight, reciprocating blade that moves up and down. They are ideal for making curved or intricate cuts and are particularly popular for cutting patterns in wood.
Key uses: Cutting curves, intricate shapes, and detailed patterns in wood.
8. Drill Presses
A drill press is a stationary machine used for drilling holes with precision. It allows for greater accuracy in depth and alignment than handheld drills. Drill presses come in various sizes, from small benchtop models to larger industrial machines.
Key uses: Drilling holes, sanding, and mortising operations.
Benefits of Woodworking Machinery
1. Increased Productivity
Woodworking machinery, particularly automated systems, dramatically increases the speed and efficiency of production. Machines can work continuously without fatigue, producing high volumes of work in a fraction of the time compared to manual methods. This increase in productivity is essential for both small businesses and large-scale manufacturers.
2. Enhanced Precision
The introduction of CNC machines has transformed woodworking by providing precise and consistent results. With computer-controlled machines, even the most intricate designs and cuts can be replicated with minimal variation. This has been especially beneficial in the production of custom furniture, cabinetry, and architectural woodwork.
3. Safety
Modern woodworking machinery comes equipped with safety features that help reduce the risk of accidents. Machines are designed to protect operators by incorporating guards, emergency shut-off switches, and automatic braking systems. However, safety training and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are still essential to prevent accidents in the workplace.
4. Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in woodworking machinery can be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced labor costs, faster production, and fewer errors make it a worthwhile investment. With automated systems, businesses can produce high-quality products at lower costs, increasing their profitability.